Understanding Article 370: A Pillar of Indian Constitutional History
In the annals of Indian constitutional law, few provisions have stirred as much debate, controversy, and historical significance as Article 370. Enshrined in Part XXI of the Indian Constitution, this article granted special autonomous status to the region of Jammu and Kashmir, altering the dynamics of governance and political autonomy in the region.
Origins and Historical Context:
Article 370 was introduced to the Constitution of India in 1949, with the primary objective of granting a special status to the state of Jammu and Kashmir. It allowed the state to have its own constitution, a separate flag, and autonomy over internal administration, except in matters related to defense, foreign affairs, finance, and communications.
Key Provisions and Implications:
Under Article 370, the state of Jammu and Kashmir had its own constitution, a separate set of laws, and enjoyed a degree of autonomy unparalleled in other Indian states. This autonomy extended to residency laws, property rights, and governmental authority within the state.
However, over time, debates arose regarding the effectiveness and necessity of such special provisions. Critics argued that Article 370 perpetuated separatism, hindered development, and impeded the integration of Jammu and Kashmir into the Indian Union.
Repeal and Impact:
In August 2019, the Indian government, under Prime Minister Narendra Modi, abrogated Article 370 through a presidential order. This bold move sparked widespread debate, both nationally and internationally, and triggered mixed reactions within the region.
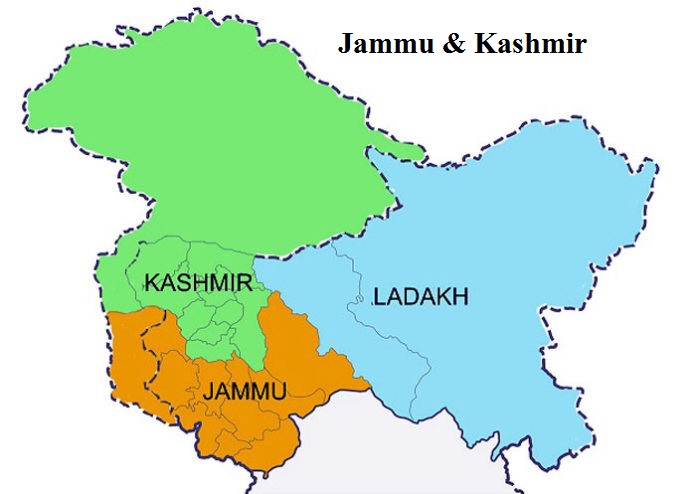
The revocation of Article 370 meant the integration of Jammu and Kashmir more firmly into the Indian Union. It also led to the bifurcation of the state into two separate union territories—Jammu and Kashmir, and Ladakh—a decision aimed at fostering better governance, development, and security in the region.
Controversies and Perspectives:
The abrogation of Article 370 was met with various reactions. Proponents viewed it as a step towards greater national integration, economic development, and the extension of equal rights to the residents of Jammu and Kashmir. However, critics raised concerns about the legality of the move, potential unrest in the region, and the implications for the socio-political fabric of the area.
Looking Ahead:
The journey of Article 370, from its inception to its abrogation, remains a pivotal chapter in Indian constitutional history. Its impact continues to shape narratives surrounding federalism, autonomy, and the complexities of governance in a diverse nation like India.
As the region adapts to the changes following the abrogation, the focus shifts toward ensuring inclusive development, fostering peace, and rebuilding trust between the people and the administration.
Abrogation of Article 370:
The abrogation of Article 370 was announced through a presidential order, accompanied by the bifurcation of the state into two separate union territories—Jammu and Kashmir, and Ladakh. This move led to the direct application of the Indian Constitution to the region, bringing it in line with the constitutional framework applicable to other states and union territories of India.
Immediate Ramifications:
The abrogation sparked a range of reactions both within the region and on the national and international stages. While supporters hailed it as a necessary step toward integration, equality, and development, critics raised concerns about the manner in which the decision was executed, potential unrest, and the impact on the region’s identity and autonomy.
Transition and Changes:
Following the abrogation, the region underwent significant changes in governance, administration, and laws. The central government aimed to accelerate development initiatives, enhance security measures, and extend various central laws and provisions to the newly formed union territories.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The aftermath of the abrogation brought forth a mix of challenges and opportunities. Challenges included addressing security concerns, restoring normalcy, and rebuilding trust among the residents. Meanwhile, opportunities emerged in terms of economic development, increased central government investment, and the potential for better integration into the national mainstream.
Continued Relevance and Future Prospects:
The abrogation of Article 370 continues to shape the socio-political discourse in India. Its repercussions, including ongoing debates, legal challenges, and efforts towards inclusive development, remain key aspects that will define the region’s trajectory in the coming years.










